The main functions of mentoring are to:
Provide a structured, one-to-one relationship or partnership that focuses on the needs of the mentored participant.
Foster caring and supportive relationships
Encourage individuals to develop to their fullest potential.
Help individuals to develop their own vision for the future.
To be a strategy to develop active community partnerships.
Mentoring
Key steps in starting
Key steps in starting
a mentoring program:
- a. Create a statement of purpose and long-range plans.
- b. Devise a recruitment plan for both mentors and participants.
- c. Develop an orientation for mentors and potential participants.
- d. Conduct an intense eligibility screening for mentors and participants.
- e. Devise a training curriculum and train mentors and participants.
- f. Create a matching strategy and criteria to pair mentors and participants.
- g. Mentor progress.
- h. Provide on-going training, materials and general support.
- i. Evaluate
Events
Upcoming YCW Workshops
Children Workshop
Children Workshop is an event where the issue of Child Safety is discussed whether online or offline. As guided by a dedicated Chaperon, children discuss the issue of child abuse and safety in their schools and communities.
Join Next Workshop
Parents Orientation
We have huge responsibility as parents and responsible citizens to safeguard children and to educate them necessary skills needed to be safe. At YCW Nigeria, we designed a session where we interact with parents on Child Safety.
Register to Participate
Annual Conference
We gathered children and teenagers together annually to discuss solutions to child abuse and encourage them to be voices in their schools and communities against abuses and violence. Children are our speakers during this event.
Register to Participate
Gallery
Past Events

ICT Access for Girls
Casey Ernest Onyeka posed with the students of Christ the King's College, Onitsha after the successful completion of National ICT Project

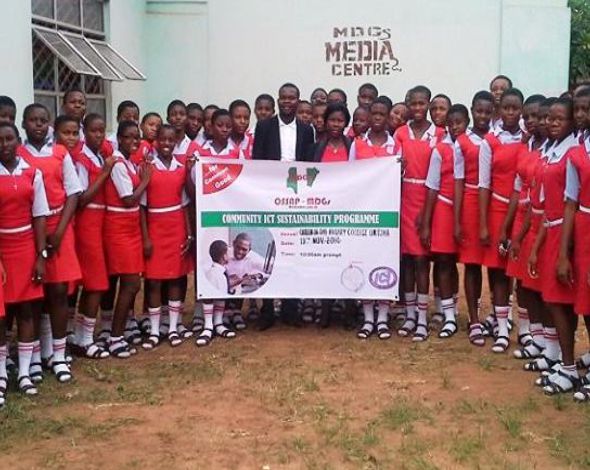
Secure Africa
Students from Royal Family Academy participated in the Africa Regional Youth Crime Prevention and Development Conference.
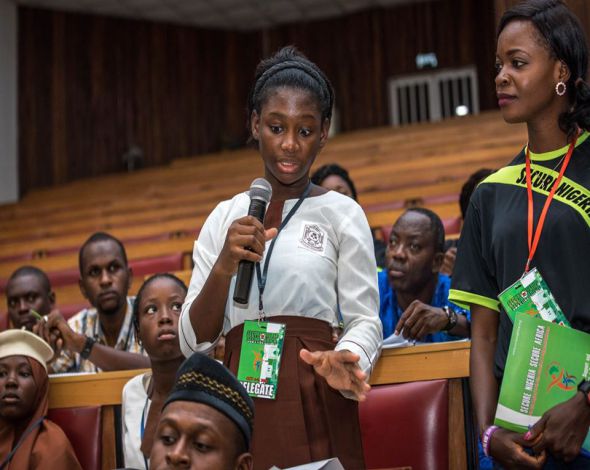

Violence Against Children
A female student of the Government Secondary School, Wuse, Abuja addressing the audience during the last Secure Africa conference held in Abuja.
#
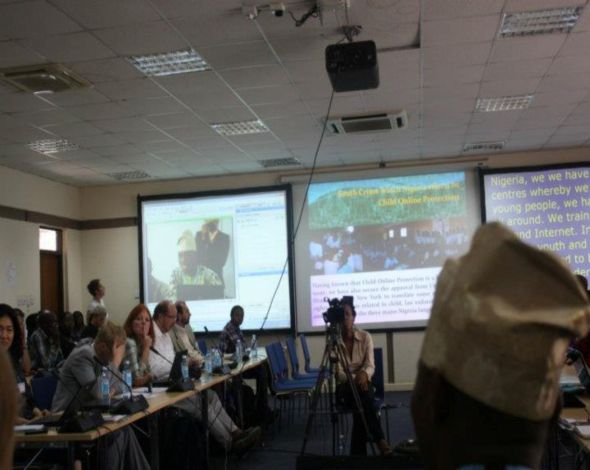

Internet Governance Forum
The Country Director, Casey 'Gbenga Adeleye making presentation at the Global Internet Governance Forum held in Nairobi, Kenya
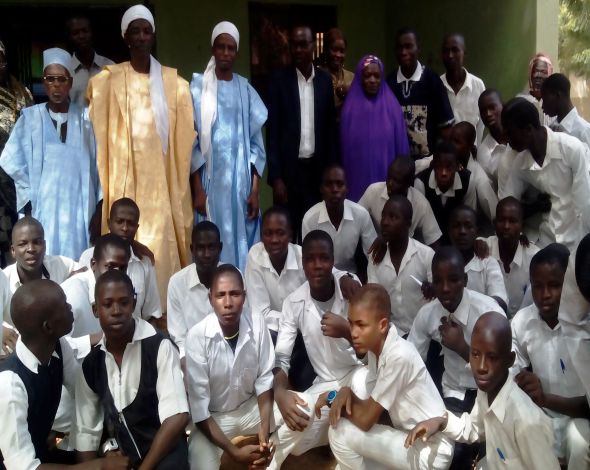

ICT Sustainability Project
The Zamfara State Commissioner for Education posed with students during the commissioning of the ICT Library Centre, DGSS Bungudu
WE ARE A LEADING CRIME PREVENTION AND PUBLIC SAFETY ORGANIZATION IN NIGERIA
Always at the forefront of
Crime Prevention, Education and Safety (Online/Offline)
GBV
Gender-Based Violence Prevention
-
Preventing GBVPreventing GBV, to stop it from happening in the first place, is a key priority. Given that GBV is based on gender norms and gender-based power inequalities, GBV prevention strategies are intrinsically linked to efforts to increase gender equality more generally. Hence, rather than disconnecting and treating GBV as a separate and isolated problem, it has to be situated in the context of gender inequalities.
-
A shift in focusA shift in focus from seeing women (and other groups exposed to genderbased violence) as victims to seeing them as survivors, actors and agents of change with a strong focus on women and girls’ empowerment and agency
-
Increase women’s political participation and influenceEfforts to increase women’s political participation and influence in contexts of peace, conflicts and other humanitarian crisis. Women have rights to participate on equal terms with men in political bodies at all levels of the society, including in peace processes. In many countries women’s political representation is very low, and women are often excluded from formal peace negotiations. This has evastating consequences for the possibility to reach a sustainable development, peace and human security
-
Efforts to increase women’s economic empowermentEfforts to increase women’s economic empowerment that enhance women’s bargaining power and ability to leave abusive relationships. This includes strengthening women’s entrepreneurship and employment opportunities, improving women’s access to land and property rights, promoting equal sharing of unpaid care work between women and men and encouraging universal access to quality education. While such efforts can contribute to increased violence against women in the short term due to gender ideals linking masculinity to the provider role, increasing women’s economic empowerment is still crucial for longer term prevention of GBV. Women’s economic empowerment interventions which also address gender norms and reach couples and communities can reduce such risks.Efforts to increase sexual and reproductive healthEfforts to increase sexual and reproductive health and rights are crucial for preventing GBV given the close relationship between the two. Such efforts include promotion and protection of women’s right to have control and decide freely over matters related to their sexuality, including sexual and reproductive health, family-planning possibilities and HIV/Aids prevention.Incorporate men and boysIncorporate men and boys as perpetrators, as victims/survivors and as agents of change. Men and boys are often neglected as survivors of GBV. Hence, there is a need to recognise and address men’s and boys’ particular vulnerabilities and needs in relation to GBV.